Providing user-friendly products and services forms the primary aspect of all business organizations. Design Thinking helps innovators and manufacturers to design as well as create products and services that meet the requirements of the customers. It is a customer-focused mindset that applies to an organization in various stages. The Design Thinking approach when applied correctly results in creating better products and services for the users of the organization. This approach incorporated in the organization using several Design Thinking Tools which find their uses in different stages of Design Thinking.
Jump ahead to
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a process of formulating innovative and creative solutions to problems faced by organizations trying to create products and services for their customers. The Design Thinking process allows organizations to understand the user requirements properly, design and test products quickly, while rapidly formulating effective solutions to problems. It is a flexible process that allows design thinking teams to go back and forth between the various stages of Design Thinking.
Stages of Design Thinking
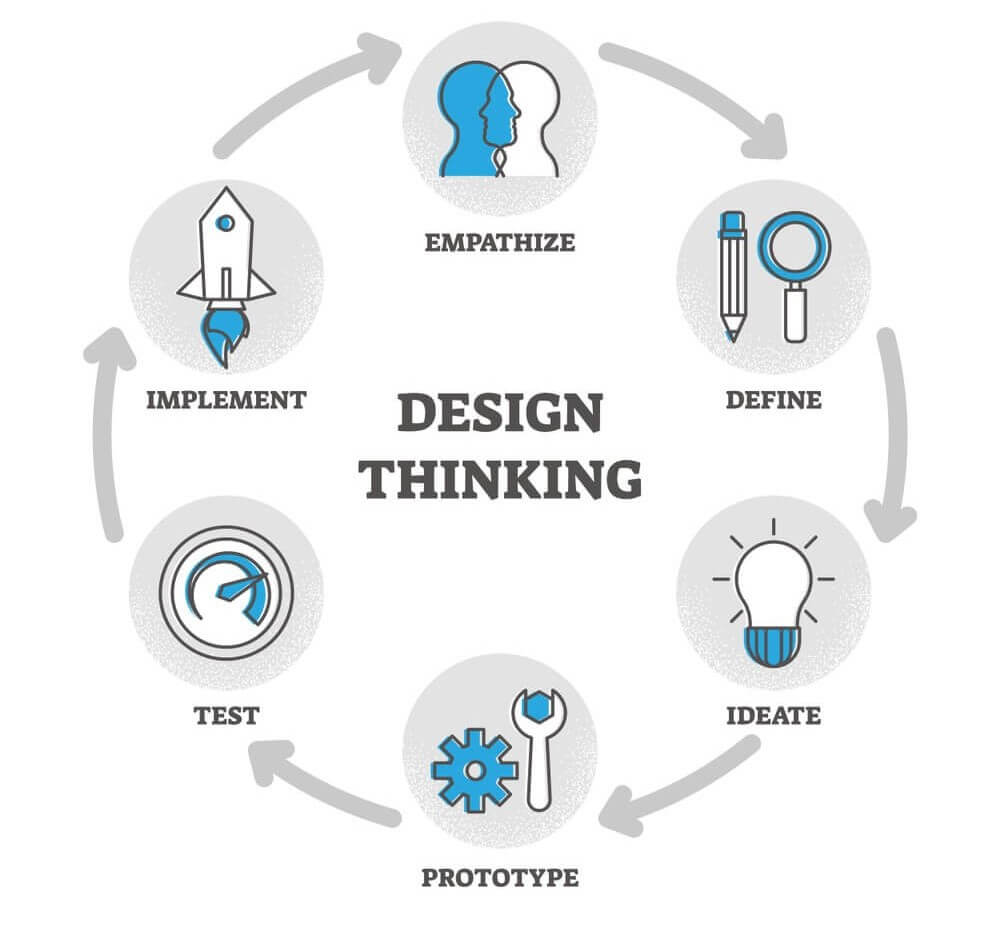
As discussed above, Design Thinking is a non-linear process that is executed through various stages. There are five stages in Design Thinking:
- Empathize
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
Each stage of Design Thinking has its own set of Design Thinking Tools available in the market that are used to solve problems and find effective solutions.
Design Thinking Tools used in the five stages of Design Thinking
Empathize
The first stage of Design Thinking is crucial as every product development process needs research. This stage focuses on empathizing with the users and understanding their needs. Also, their expectations from the products or services that the organization is thinking of releasing.
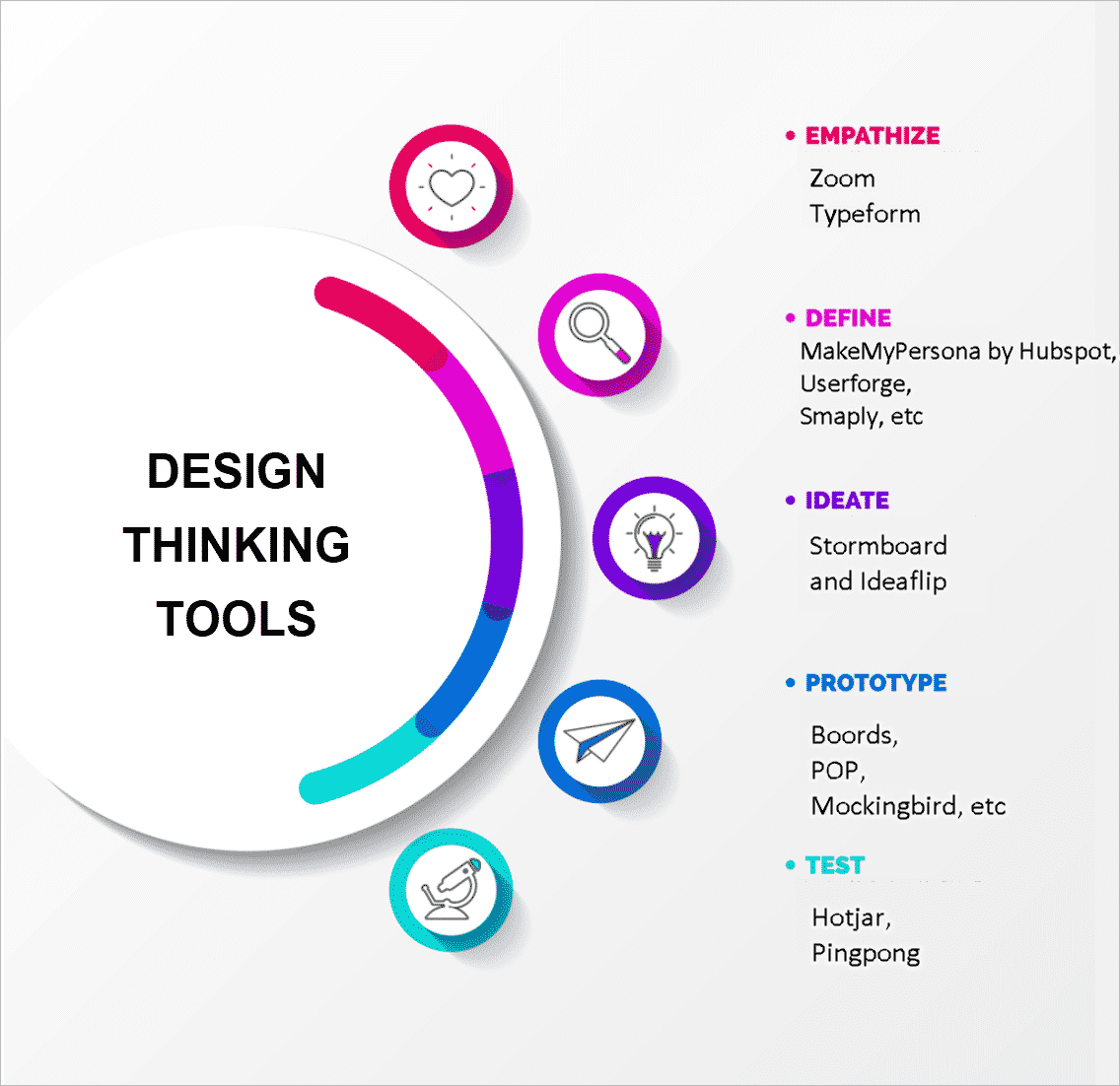
Design Thinking Tools like Zoom and Typeform can be used to interact with users directly or indirectly using chats, surveys, etc.
The main objective of this stage is to try and gather as much information as possible to understand the user requirements. Since Design Thinking is human-centered, being able to empathize with the customers, eliminates pre-conceived notions and assumptions about their real needs.
Define
At this stage of Design Thinking, data collected from the empathize stage is analyzed to define the core problem area. These are also called problem statements. Design Thinking allows organizations to assess their existing strategies. it also rectify their processes to match their customer requirements. The problem statements should reflect all the challenges affecting the customers. Thus, creating personas for different users and their specific requirements and expectations will be helpful in categorizing and finding patterns. This will help in summarizing the problems in the problem statement.
Some examples of Design Thinking Tools used for defining the problem used by organizational teams are MakeMyPersona by Hubspot, Userforge, Smaply, etc.
Ideate
After understanding the problem and defining them clearly in the problem statement, design thinking teams can move on to ideating. The process should focus entirely on solving the problem faced by the users. Generating ideas that are innovative and new is the prime objective here. At this point, brainstorming with teams is done to come up with approaches to develop the good or service that successfully answers the issue. one may utilize ideation tools like Ideaflip and Stormboard to generate unique ideas. The ideate stage allows design thinking teams to generate as many ideas as they can find to solve the problem. The most effective solution selected from these and advanced to the next level.
Prototype
The ideas that best manage to solve the problem can be designed and developed during this design thinking stage. Prototypes will allow teams to assess their effectiveness in solving the problems. Design Thinking Tools like Boords, POP, Mockingbird, etc. can help create prototypes to get a picture of the real product. It is an experimental stage, so the prototype does not have to be of high quality or working. Teams can decide whether to continue with the prototype or reject them based on their success rate.
Test
Teams may extensively test prototypes throughout the design thinking stage before developing the final product design. Since design thinking is a non-linear process, teams can go back and forth, adjust, and alter the process to find an effective solution to the problems any time they want. Testing can be done using design thinking tools like Hotjar and Pingpong.
Although Testing might look like the final stage of Design Thinking, this is not the final step as new insights found during this stage can again be used to design the final product.
Apart from the above-mentioned Design Thinking Tools, there are several standalone apps and online tools available in the market that allows business enterprises to carry out the entire Design Thinking process like Sprintbase and InVision.
Conclusion
Any organization or business enterprise that is user-based has a need for proper Design Thinking. Using Design Thinking Tools, organizations can make tailor-made products and services for their customers. Design Thinking is one of the best approaches to creating products and services that will effectively meet the requirements of the end-users. Thus, helping the organizations achieve their goals and objectives.
Summary:
By identifying needs before developing solutions, design thinking is a user-focused method that helps teams solve real-world problems. Its five adaptable stages are empathizing with users, defining challenges, generating ideas, prototyping solutions, and testing them for feedback. Each stage is supported by tools like Miro, Typeform, Boords, and Mockingbird, which streamline and enhance the process. Workflow management is facilitated by end-to-end platforms such as Sprintbase or InVision. Effective use of these tools can boost creativity and improve results. To strengthen your skills and apply these methods in real projects, explore our Design Thinking Certification Training.
FAQs on Stage-Wise Design Thinking Tools:
1. What are the tools used in the design thinking process?
Tools include empathy maps, customer journey maps, personas, brainstorming techniques, affinity diagrams, and rapid prototypes to solve problems effectively.
2. What are the 5 stages of design thinking?
The five stages are Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test, providing a structured approach to user-centered innovation.
3. What is the use of design thinking?
Design thinking helps teams understand user needs, generate creative solutions, and improve decision-making for real-world problems.
4. Which tool is used in the design (ideation) phase?
Brainstorming, mind maps, SCAMPER, and “How Might We” questions are commonly used to explore multiple ideas quickly.
5. What are the uses of design tools?
Design tools help organize insights, create prototypes, visualize solutions, and validate ideas efficiently.
6. What are the 7 steps in the design process?
The seven steps are research, ideation, concepting, prototyping, testing, implementation, and review, ensuring thorough design development.
7. Can design thinking be nonlinear?
Yes, it’s iterative; teams often revisit stages to refine ideas based on new insights or user feedback.
8. Which software tools are popular for prototyping?
Tools like Figma, InVision, Justinmind, and FigJam allow designers to create and test digital prototypes quickly.
9. How do you empathize effectively with users?
Conduct interviews, surveys, observations, and empathy mapping to deeply understand users’ behaviors and challenges.
10. What is an affinity diagram and when to use it?
An affinity diagram organizes large amounts of qualitative data into themes to identify patterns and insights.
11. What is mode mapping in design research?
ModeMapping tracks users’ mental “modes” to highlight unmet needs and design opportunities.
12. How can Design Thinking Certification help in applying these tools?
The certification teaches practical use of all design thinking tools and stages, helping professionals apply them confidently in real projects.