The digitization era has enabled organizations to store their customers’ data without any time limit. Several websites we visit today on smartphones and tablets extract all sorts of information from the device without our permission. This causes stringent data protection laws to come into force through the 7 GDPR Principles. Every nation has formulated data protection laws based on the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
GDPR was enforced in 2018 by the European Union. The GDPR law is designed to protect the personal data of citizens. Organizations catering to the needs of EU citizens require approvals from customers before collecting their data. In addition, businesses need to be transparent with their customers while using their data. The regulation is based on a set of principles that guides an organization regarding data protection law.
Previously, the Data Protection Act of 1988 was based on eight principles. The evolution of information technology has led to the refinement of these eight principles and reduced its number to 7. Let us gain a deeper understanding of these principles and determine their significance.
Jump ahead to
7 Principles of GDPR
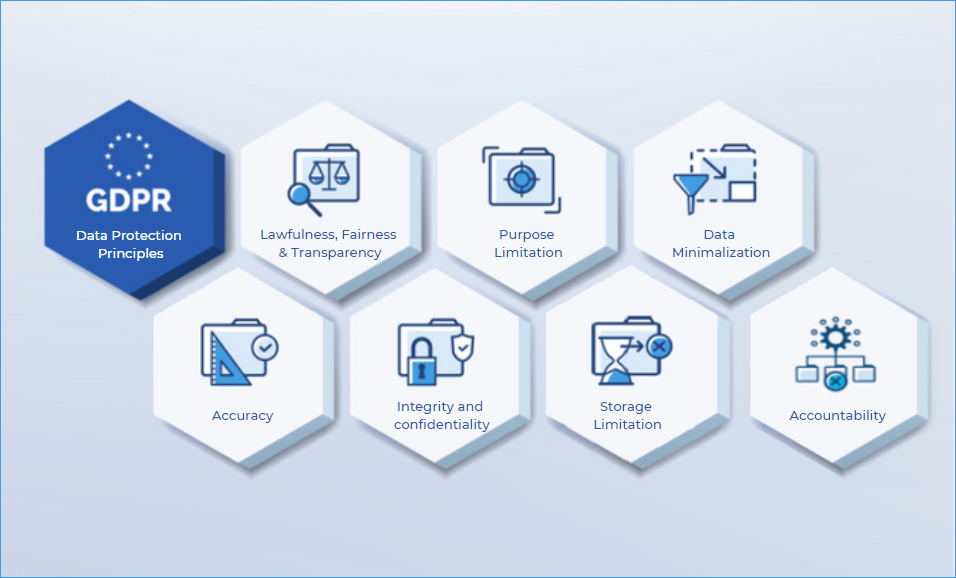
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
This principle of GDPR emphasizes collecting information legitimately, using it as promised, and maintaining transparency. Lawfulness further indicates that the data is obtained with consent or through a contract, and so on. Fairness states that the data collected should be processed as promised to the customer. Transparency is vital for individuals as it helps them understand their data protection rights and provide consent accordingly.
Purpose Limitation
Organizations that collect personal data must explicitly inform how the data is being processed along with the purpose. On receiving consent, businesses cannot alter the purpose for which data was collected. This GDPR principle demonstrates that an organization can process the data collected only for the purpose disclosed to customers. If the data collected is needed for a different purpose, businesses need to receive the approval of individuals.
Data Minimalization
This GDPR principle specified that the data collected should be sufficient and relevant. The law requires businesses to justify the data collected along with necessary documentation. Organizations that collect data on EU citizens are allowed to gather only the primary data of citizens to fulfill the stated purposes. If any organization is observed to cross the limit of collecting data, it is seen as violating the regulation. Furthermore, the law encourages businesses to fulfill their requirements without collecting personal data.
Accuracy
The accuracy principle of GDPR requires businesses to maintain up-to-date information on individuals. Owning irrelevant information on individuals is further considered a violation of the regulation. Such data have to be deleted from the organization’s database. Businesses that often require the personal data of individuals can add that clause to their data policy. Furthermore, even customers can impose their rectification rights and get the previous data deleted from the database.
Storage limitation
This principle of GDPR limits the period for storing the personal data of organizations. The data collected with consent from individuals has an expiration date. Beyond the time limit, organizations lose the right to store the data of individuals. Further, it is advised to inform the individuals about this limitation date. Businesses need to have a proper data deletion system in place to erase the collected data. Failing to do so is considered a violation, wherein organizations might end up paying huge fines.
Integrity and confidentiality
Every organization following the principles of GDPR is bound to secure the data collected from individuals. As cyber-attacks have increased, organizations are held responsible during a data breach. Hence, businesses are required to safeguard the personal data of individuals through a robust information security system. Adequate cybersecurity measures are a must for organizations dealing with the sensitive information of individuals.
Accountability
This principle of GDPR requires organizations to be reliable and accountable while collecting the personal data of individuals. To avoid violations, Businesses need to document every step while processing the data collected to prevent breaches. This practice allows organizations to justify their practices when charged with non-compliance.
Businesses that fail to follow the rules specified in GDPR must pay substantial non-compliance acceptable amounts. The fine may range from the range anywhere between 17.5 million euros to 4% of the annual income, along with other penalties. As a result, organizations need to comply with the regulation and implement the principles while transacting with EU citizens.
Conclusion
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a law that gives individuals more control over their personal data and requires businesses to be more transparent and open about how they use it. The complexity of the regulation has necessitated organizations to hire professionals well-versed in GDPR. These professionals own the certification of GDPR Certified Data Protection Officer. Indulging in earning GDPR CDPO Certification helps individuals gain in-depth insights into GDPR practices and principles. The practices can be further implemented in organizations while collecting the personal data of individuals.


