With advancements in technology, change is inevitable. Organizations constantly strive to adapt and sustain in the market. This necessitates businesses to implement change management and implement change management models. In the past era, the main priority of a business was stability. Organizations that don’t bring change can hardly survive in the industry for longer. Therefore, businesses need to have a rigorous change management system in place.

Jump ahead to
What is Change Management?
Change management refers to businesses modifying the current procedures and capturing new opportunities. The external and internal influences require businesses to change the organizational structure and job roles. Hence, the change management efforts must be monitored and evaluated regularly. Furthermore, businesses need their employees to accept change before implementing change management. Employee resistance can complicate the change management process and disrupt its functioning.
What is the purpose of managing change?
Businesses cannot directly instil change and ask the employees to follow. For a smooth transition, businesses must ensure that all employees welcome change. Employees are key drivers of a business. As a result, they must have a comprehensive understanding of the change. Also, organizations should formulate the exact reasons for implementing change and its effect on day-to-day operations. Change management was introduced to address these issues. Various models were created to suit the needs of the organization. This enabled businesses to bring change into the organization without major obstacles. Let us have a look at a few of these models.
Change Management Models
Several models have been created to assist organizations in managing change. Each model is designed to suit the company’s values and change the objectives and goals of the organization.
Top 5 Change Management Models
Kotter’s Model
This change management model is widely used globally. It focuses on how employees respond to change. The theory is based on implementing different stages determining employees’ reactions to change. Kotter’s model assists businesses in directing employees to change their perspectives. Furthermore, any organization can easily incorporate this model. The 8 stages are as follows:
- Creating urgency
- Build a change team
- Forming the vision
- Communicate
- Remove barriers to change
- Focus on short-term wins
- Maintain the acceleration
- Institute the change
ADKAR Model
Jeffery Hiatt introduced the ADKAR model. This model emphasizes people who bring change. ADKAR represents Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement. These are the goals that the business must accomplish. Change managers communicate with employees and make them aware of the changes. After that, the change team convinces employees by stating the benefits. As it is a model based on people, businesses can easily implement and sustain change for longer. Small businesses can make use of this model to manage change. The stages involved in this ADKAR model are as follows:
- Awareness
- Desire
- Knowledge
- Ability
- Reinforcement
Lewin’s Model
Kurt Lewin developed the model. In this model, Lewin explains breaking down the changes into three phases. The three phases include Unfreeze, Change, and Refreeze. Change managers need first to unfreeze a certain process. This helps to determine why the change is needed. The second step is to implement the change and evaluate it. The final step is to refreeze the process after considering feedback from employees. Although this model slows down the change management process, it assists in overcoming resistance towards change.
McKinsey 7-S Model
This model is used to implement change management in the whole organization. It is one of the complex models that has lasted longer than other change models. The 7S model identifies the seven fundamentals of every organization. Businesses focus on how these elements affect each other to identify their weaknesses. The 7S includes.
- Strategy
- Structure
- System
- Shared Value
- Style
- Staff
- Skills
Among the 7 elements, change managers can easily identify strategy, structure, and system. The rest are relatively difficult to determine as they depend on other factors. Change managers need to devise ways in which these elements are connected. Changing one of these elements can disrupt the other 6 elements. Finding the weakness assists in implementing change effectively.
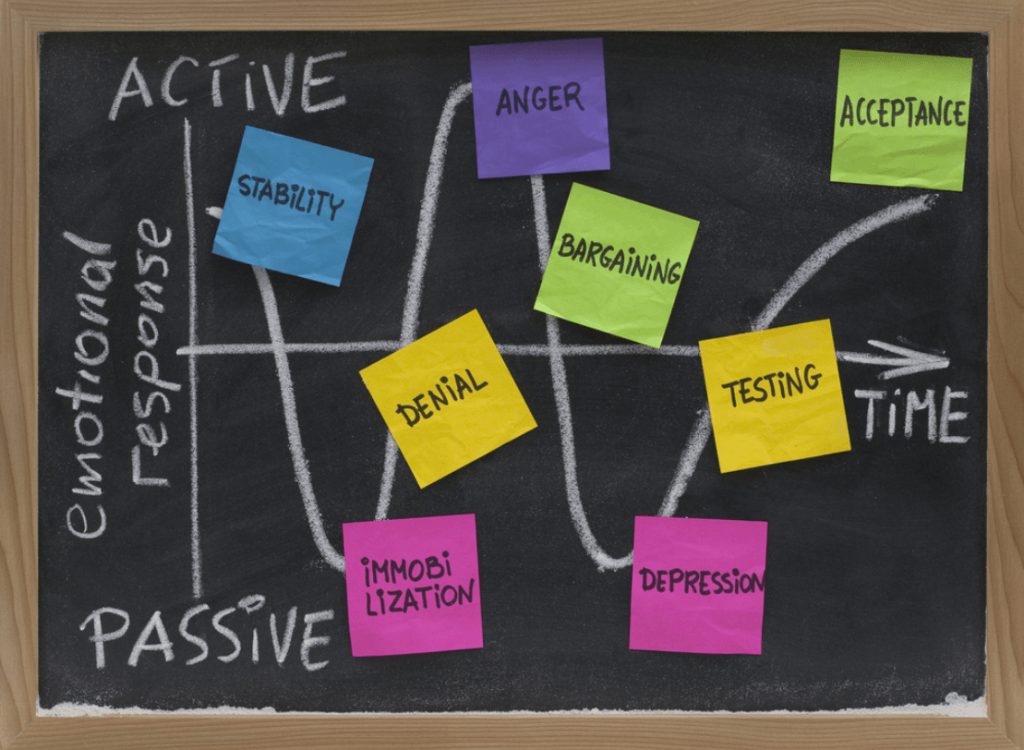
Kubler-Ross Model
This change model focuses on employees only. Businesses implement this model to know their employees better and cater to their needs. It is believed that during the implementation of change, employees undergo 5 stages. They are:
- Denial
- Anger
- Bargaining
- Depression
- Acceptance
Businesses can empathize with employees and their feelings during the change, from denial to acceptance. Acknowledging these emotions can help businesses to remove the biggest barriers to change Management. Small organizations can apply this model as employees are fewer in number. Kubler-Ross’s model further strengthens the bond between employers and employees.
Conclusion:
Change management is essential for businesses to survive in the industry even in the distant future. Businesses are required to choose the best change model that suits the organization. The change management process is supervised by PMP Certified project managers and carried out by the change team. Project management professionals must ensure that the change is instilled successfully. Furthermore, change management can only occur when the whole organization is involved.
Summary:
Understanding change management models is essential for organizations aiming to navigate transitions smoothly and improve performance. These are the five most popular change management models, including Lewin’s Model, ADKAR, Kotter’s 8-Step Model, McKinsey 7-S Framework, and Bridges’ Transition Model. Each provides a structured approach to guiding individuals and teams through change. These models help reduce resistance, maintain productivity, and ensure successful adoption of new processes. Boost your expertise with Unichrone’s Change Management training and drive impactful transformation in your organization!
FAQs on Popular Change Management Models:
1. What is Change Management?
Change management is the process of guiding an organization and its employees through transitions to modify current procedures and capture new opportunities.
2. What are the 5 most popular change management models?
The most popular models are Kotter’s 8-Step, ADKAR, Lewin’s Three-Step, McKinsey 7-S, and the Kubler-Ross Change Curve.
3. What are the 8 steps in Kotter’s Model?
The 8 steps start with creating urgency and building a guiding coalition, leading up to instituting the change firmly within the culture.
4. What does ADKAR stand for in change management?
ADKAR is an acronym for Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement, which are the goals required for individual change success.
5. What are the 3 stages of Lewin’s Change Model?
The three phases are Unfreeze (preparing for change), Change (implementing the process), and Refreeze (stabilizing the new process).
6. Which change model focuses on organizational elements?
The McKinsey 7-S Model focuses on the seven interconnected elements of an organization: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills.
7. Which model addresses employee resistance to change?
The Kubler-Ross Model specifically addresses the emotional stages employees go through during change, from denial to final acceptance.
8. What is the purpose of the Unfreeze stage?
The Unfreeze stage’s purpose is to prepare the organization for change by challenging the current stability and determining the need for transformation.
9. What are the 5 stages of the Kubler-Ross change curve?
The five stages are Denial, Anger, Bargaining, Depression, and finally, Acceptance.
10. What is the primary benefit of using a change management model?
The primary benefit is ensuring a smooth transition by reducing employee resistance and aligning all organizational efforts toward the new objective.